OAuth Credentials
OAuth Credentials can be defined in the Credential Manager and then referenced by database credentials through the use of environment variables or used in other credentials.
Two OAuth credential flows are supported: Client Credentials and Authorization Code.
Example 1 - Client Credentials
In this example an OAuth credential is defined using Client Credentials that will obtain an Access token from Azure Entra. This token is then used to populate the environment variable %OAUTH_TOKEN%.
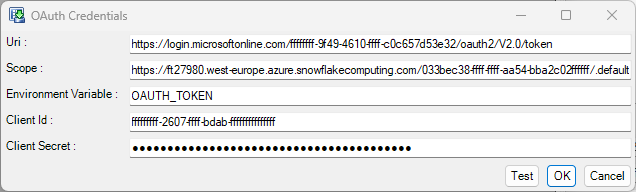
The database credential can then be specified using the %OAUTH_TOKEN% environment variable:
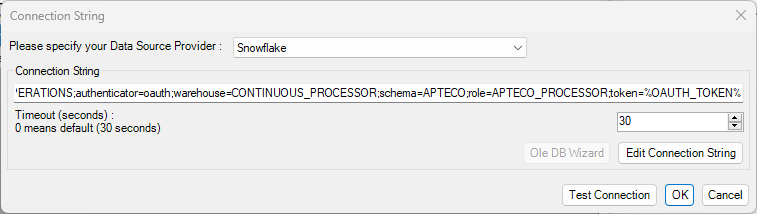
Whenever a connection to the data source is required by FastStats Designer then the OAuth credential will re-authenticate to generate a new access token for the data source connection.
Example 2 - Authorization Code
For the Authorization Code flow the OAuth details are entered and then the ‘Get Refresh Token’ button is clicked:
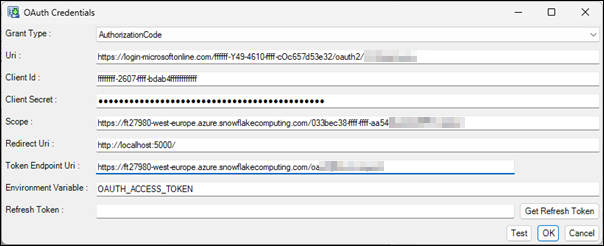
A browser window will appear to allow you to perform the authentication. Once authentication is successful then the browser will be redirected to the Redirect Uri so that FastStats Designer can capture the OAuth Refresh Token. Typically Refresh Tokens will last indefinitely if they are regularly used, but will expire after 90 days if left unused.
FastStats Designer will used the long lived Refresh Token to obtain a short-lived Access Token to authenticate against the required service.
OAuth credentials can be used for Data Source connections via the Environment Variable, the OAuth credential will populate the environment variable with an Access Token and then this Environment Variable can be in the data source connection string.
OAuth credentials can also be used for SMTP (Email) connections and in Salesforce connections.